
Human aging is inevitable, but you can determine the rate of aging, so we need antioxidant properties!
How to effectively resist oxidation
What is antioxidant? Simply put, antioxidant is the process of clearing free radicals.

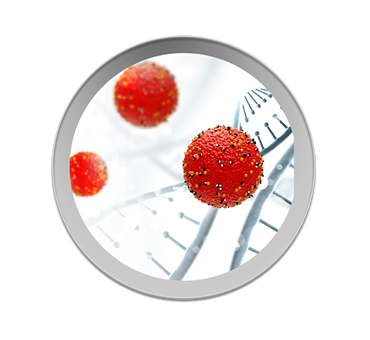
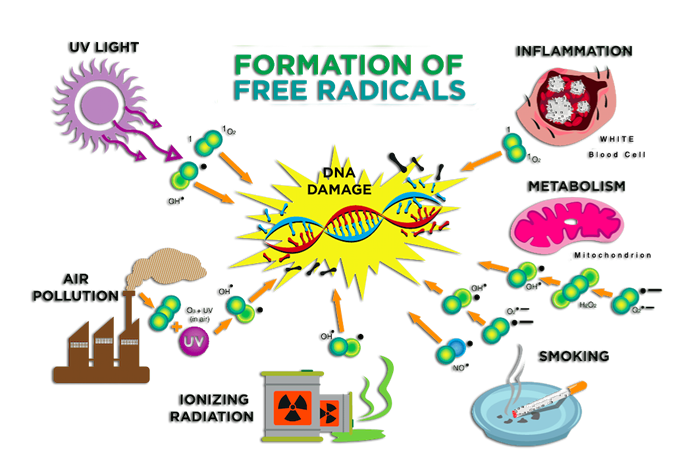
Free radicals are by-products of normal cell activity, with unstable structures that often interfere with and affect other normal and healthy cells. They are also the root cause of diseases. They are oxidizing and highly aggressive, and can snat om other atoms. Atoms that have been snatched away will also snatch electrons from other atoms.
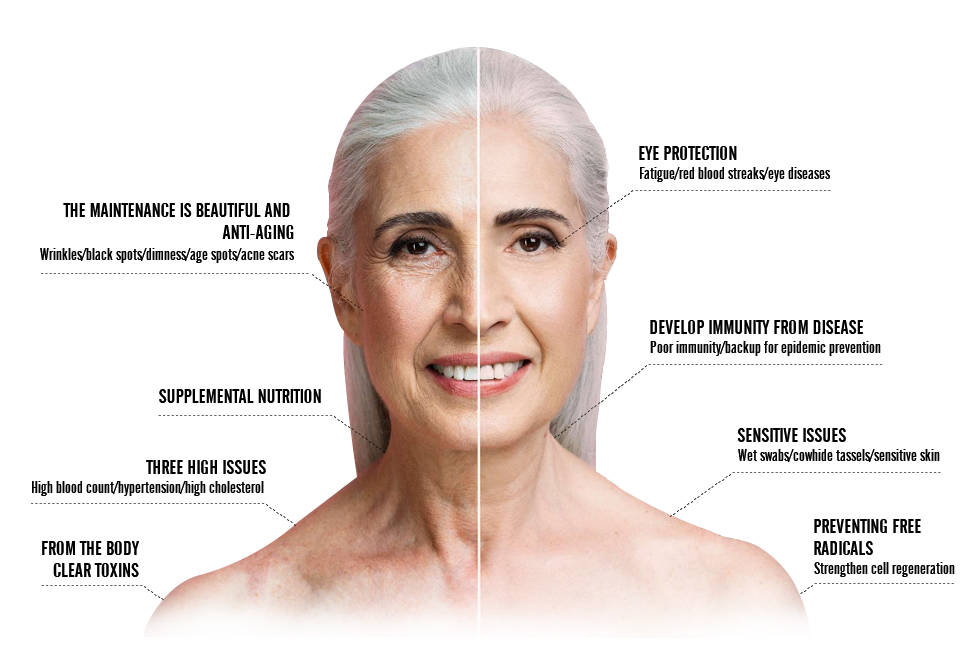
Excess free radicals damage healthy cells, such as damaging cell membranes, causing skin aging and wrinkles, damaging proteins, causing organ decline, damaging fats, causing arteriosclerosis, and damaging DNA, leading to cancer. Therefore, antioxidant activity is aimed at reducing the production of free radicals, reducing the damage caused by free radicals to body cells, and achieving the effect of delaying aging.
1、Damaging genetic factors, DNA, causing DNA strand breaks or base modifications.
2、Disrupting unsaturated fatty acids, leading to lipid peroxidation.
3、Attacking protein molecules, oxidizing internal enzymes, rendering serum antiproteases inactive.
4、Stimulating abnormal reactions in monocytes and macrophages, causing them to release inflammatory agents, leading to inflammation.
5、Attacking the body's periodontal tissues, breaking down osteoclasts and the bone matrix at the bone interface.
6、Oxidizing lipids, resulting in cellular degeneration, deformation, and death, contributing to the aging of bodily tissues and organs.
7、Directly impacting cell nuclei, causing genetic mutations and potentially triggering cancer.
8、Inflicting damage on organs such as the heart, liver, and lungs, as well as blood vessels.